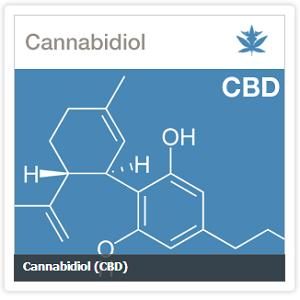
A new study published by the journal J-Stage, and funded by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, has found that cannabinoids - whether THC, CBD or CBDV – were effective at blocking a certain enzyme which is known to cause cancer, and is produced in large amount when cigarettes are consumed.
“These results suggest that the pentylresorcinol structure in CBD may have structurally important roles in direct CYP1A1 inhibition, although the whole structure of CBD is required for overall inhibition”, according to researchers.
CYP1A1 is an enzyme which isn’t dangerous at low-levels, but is produced in large quantities when someone smokes cigarettes; at large doses, the enzyme has been linked to cancer.
Researchers state that; “Accordingly, CBD and its related compounds, which are potent inhibitors of CYP1A1 activity, would be useful as a lead compound in anticancer chemotherapy.”
Source: TheJointBlog.Com